ADK Synergies
Vitamins A, D3, and K2 (or ADK) work in concert for many aspects of health. All three must be in balance for effective results in various parts of the body. In this post we highlight the overlapping and synergistic benefits between the three vitamins. More details are available in the post for each respective vitamin. Vitamin D takes center stage as it has multiple links to both Vitamin A and Vitamin K. In some cases all three play a role in supporting functions in the body.
Benefits of ADK
These three vitamins are very much interdependent. Vitamin A is an essential factor in Vitamin D’s hormonal function and K2 is necessary to activate the proteins made in response to Vitamin A and Vitamin D. Vitamin A, Vitamin D3, and Vitamin K2 all promote a healthy immune system and supports bone development and strong teeth.
Immune System
 Several immune system functions depend on Vitamin A. Genes involved in immune responses are regulated by Vitamin A.1 It is essential for preventing serious conditions like cancer and autoimmune diseases, but also common illnesses like the flu or common colds. Vitamin A ensures better immunity by keeping the mucus membranes moist and enhances the activity of white blood cells.
Several immune system functions depend on Vitamin A. Genes involved in immune responses are regulated by Vitamin A.1 It is essential for preventing serious conditions like cancer and autoimmune diseases, but also common illnesses like the flu or common colds. Vitamin A ensures better immunity by keeping the mucus membranes moist and enhances the activity of white blood cells.
Vitamin D receptors are found in most immune cells. Populations with limited sunlight exposure have been found to have weakened immune systems compared to populations with greater exposure to direct sunlight. Vitamin D is believed to help maintain healthy immune cell development, differentiation and migration. Those with higher levels of Vitamin D are less likely to suffer autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes and multiple sclerosis.2 Higher levels of Vitamin D are associated with proper cytokine production which is important for signalling in the immune system. Higher serum levels are also linked to the enhancement of the body’s local antioxidant defenses.
Gas6, a Vitamin K dependent protein closely associated with the nervous system, modulates microglia which are the primary immune effectors of the central nervous system and are at the core of tissue maintenance and repair.
Bones and Teeth
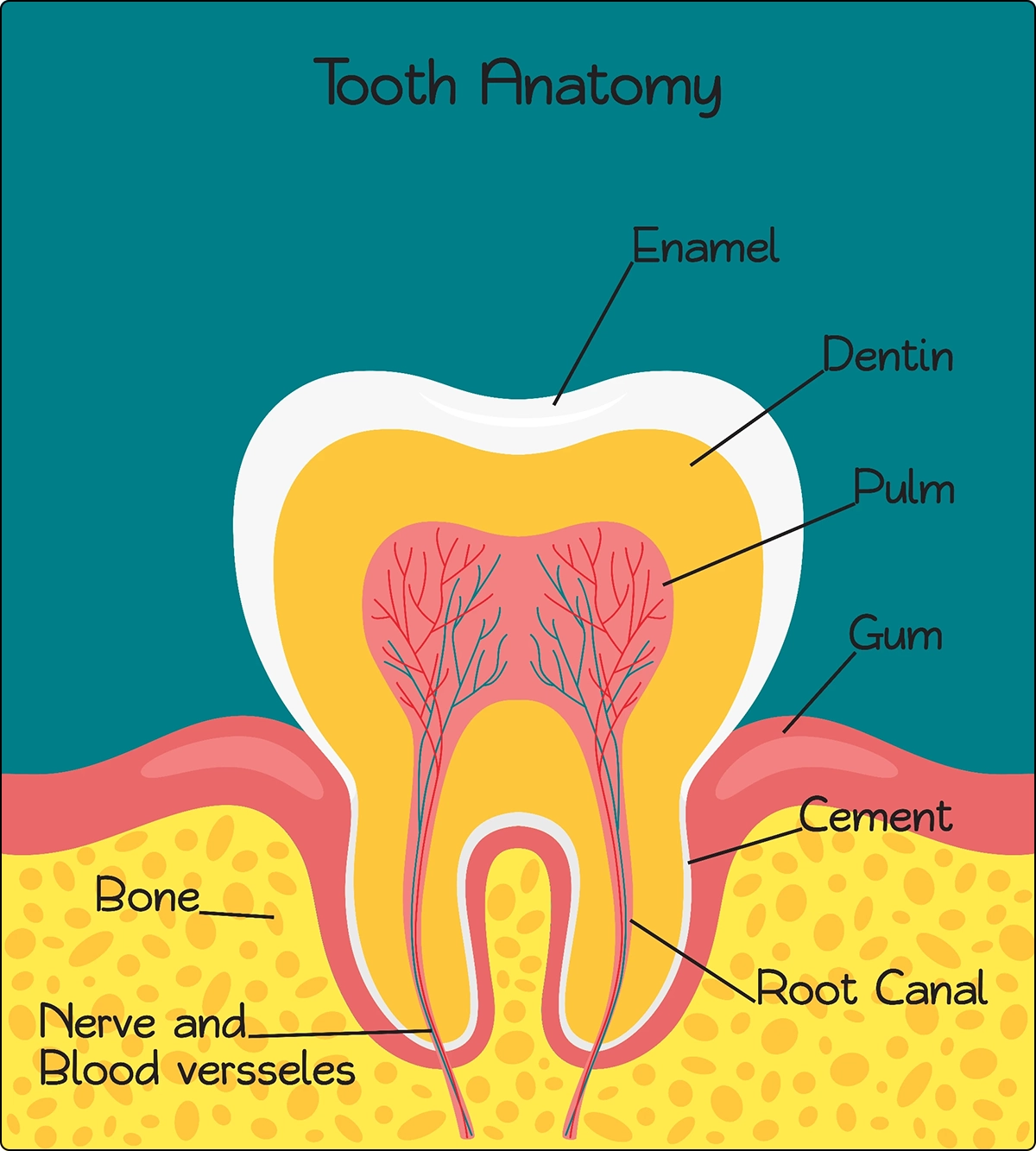
Vitamin A strengthens the teeth by helping to form dentin which is a layer of hard material just below the surface of the tooth.
Vitamin D is key for the development and maintenance of bones. It is pivotal for normal skeletal development in the womb, throughout childhood and also for adults. Vitamin D enhances intestinal calcium and phosphorus absorption and reduces urinary calcium loss. It also promotes bone health by maintaining the parathyroid hormone levels at healthy levels which stimulates bone forming activity and encourages bone mineralization.
Vitamin A and Vitamin D3 both regulate the activity of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. In some cases, their regulatory effect involves interactions between the vitamins and their respective receptors on the actual bone cells. In other ways, the vitamins modify bone remodeling indirectly.
“ .. a remarkable synergistic effect between the hormonal forms of vitamin A and D3 on the synthesis of this bone-specific protein was observed” 3
Vitamin K2 is needed to help calcium and other minerals bind into the bone matrix to strengthen bones. Otherwise these minerals will stay in soft tissue where it can cause calcification. Studies suggest Vitamin K is effective at slowing bone loss in people with osteoporosis and in some cases reversing it as well.4
Vitamin K2 maintains and improves bone mineral density. Our bones need osteocalcin to absorb calcium. Osteocalcin is released by osteoblasts (bone building cells) and binds to calcium. Osteocalcin requires Vitamin K2 to become fully activated so that it can bind to calcium.5 Osteocalcin also stimulates the growth of new dentin, which makes your teeth stronger.6,7 Dr. Weston A. Price identified Vitamin K was one of the vitamins that is vital for tooth remineralization and the prevention of cavities.
ADK Interactions
Vitamin A and Vitamin D3 aid with the formation of bone matter. Vitamin D also helps you absorb calcium while Vitamin K2 helps direct the calcium into the bones. As we can see the bone forming functions of these vitamins are inter-connected. It should also be noted that taking Vitamin D alone can cause a deficiency in Vitamin K2 because more Vitamin K2 is needed for the bone forming activities triggered by the Vitamin D. For this reason it is important to make sure you are getting enough Vitamin K2 when supplementing with Vitamin D.
Vitamin D with Vitamin A Benefits
Vitamin A has a wide range of benefits and also enables benefits of Vitamin D in our system. Research suggests that health benefits, such as improved gene function and the inhibition of prostate cancer, are maximized by the supply of both vitamins.
Gene Function
Vitamin A’s antioxidant properties support gene regulation, including genes involved in immune responses. It works against retinitis pigmentosa which a genetic disorder of the eyes that causes loss of vision. 8 Vitamin A can activate specific genes in prostate cancer stem cells that will cause those cancer cells to die.9
Vitamin D has a real effect on fetal modifications of gene expression and regulation. This could explain why it has such wide-ranging health benefits at all stages of life. Vitamin D is also involved in gene expressions for the production of dopamine, one of our feel-good neurotransmitters.
Prostate Cancer
Vitamin A seems to aid in the use of dietary protein. Androgens are steroid hormones that regulate the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates and they typically promote prostate cancer. However, Vitamin A boosts androgen production while also strongly inhibiting prostate cancer. Vitamin A can bring about the death of prostate cancer cells.10 Retinoic acid is a chemical made from Vitamin A. It can activate specific genes in prostate cancer stem cells and reduce the ability of the cancer to invade surrounding tissue.11 Findings suggest that Vitamin A related compounds can be used to enhance clinical treatments for prostate cancer.
A recent study suggests that Vitamin D receptor Taq I polymorphism might be a risk factor of prostate cancer risk, especially in Asians.12
A and D Interactions
In addition to these overlapping benefits it has been shown that moderate amounts of Vitamin D increase the body’s need for Vitamin A. It has also been shown that Vitamin A protects against the negative effects of rare Vitamin D toxicity. It makes perfect sense to supplement with both these vitamins together.
Vitamin D with Vitamin K Benefits
In addition to these overlapping benefits it has been shown that moderate amounts of Vitamin D increase the body’s need for Vitamin A. It has also been shown that Vitamin A protects against the negative effects of rare Vitamin D toxicity. It makes perfect sense to supplement with both these vitamins together.
Vitamin D and Vitamin K both contribute to proper mental health and cognition, and help preventing and reducing inflammation.
Mental Health and Cognition

Vitamin D has a positive effect on mental health by helping to produce serotonin and dopamine in the brain and protecting neurons from oxidative degeneration. Serotonin and dopamine are the neurotransmitters responsible for making us feel good. They occur naturally in the brain and help the mind to stay calm and maintain focus during tasks. They also help you to resist depression and other mood disorders.
Vitamin D may be important to producing serotonin in the brain from tryptophan. Serotonin regulates many functions including various cognitive functions, social behavior, decision-making, impulse control and aggression, memory, anxiety, and more. Vitamin D supplementation seems to decrease depressive symptoms more during the winter months.13
Vitamin D is also involved in gene expressions for the production of dopamine. Dopamine neurons are in the mid-brain and their target neurons are in the motor and rewards systems. The motor system allows us to move and the rewards system make it desirable for us to move. These neurons were found to express the Vitamin D3 receptor protein.
Vitamin D helps protect our neurons. Active Vitamin D enhances glutathione metabolism in neurons whereby it promotes antioxidant activities that protect neurons from oxidative degeneration. Vitamin D receptors have been found in areas of the brain involved in both memory and cognition. Studies have shown Vitamin D to be an essential neurosteroid hormone that plays a wide variety of protective and regulatory roles in the brain.
Vitamin K may support the nervous system by protecting it from damage caused by calcium deposits. This benefit primarily supports cognitive functions in older users.14
Inflammation

Chronic inflammation is the source of many diseases, including cancer, obesity, and heart disease. Inflammation is also a crucial component of many chronic aging diseases. Meta-analysis shows Vitamin D supplementation may reduce chronic low-grade inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes.15
Evidence suggest Vitamin K also has anti-inflammatory properties.16,17 Vitamin K dependent proteins and inflammation have been associated with cardiovascular disease and osteoarthritis, which are leading causes of disability and mortality in older adults. Low levels of Vitamin K are associated with increased bone pain.18
D and K Interaction
Taking Vitamin D alone can contribute to a deficiency in Vitamin K2 as more Vitamin K2 is needed for the bone forming activities triggered by the Vitamin D. The more Vitamin D your body has the more Vitamin K2 it needs. Vitamin D toxicity, though rare, also appears to result from a depletion of Vitamin K.
Vitamin A with Vitamin K Benefits
Vitamin A and Vitamin K both contribute to healthy and younger looking skin. They help protect from skin cancer and keep wrinkles at bay.
Skin

Vitamin A is necessary for wound healing and skin regrowth. It is needed to support the skin cells both internally and externally and is a powerful aid in fighting skin cancer.19 Vitamin A reduces lines and wrinkles in the skin by producing collagen, which is responsible for keeping the skin looking young.20 Vitamin A deficiency will lead to the drying and scaling and can also lead to acne and poor complexion.21
Vitamin K2 is also promising for skin health and anti-aging because it can help stop the accumulation of excess calcium in the skin. The excess calcium makes the skin less elastic and can contribute to wrinkles. Research has shown that Japanese women were less likely to have wrinkles than other cultures.22 Nattō, which is fermented soy containing high amounts of Vitamin K2, is common in the Japanese diet. The high Vitamin K2 content in the Japanese diet contributes to healthier skin.
Summary
The ADK vitamins are very much interdependent. Vitamin A is an essential factor in Vitamin D’s hormonal function and Vitamin K2 is necessary to activate the proteins made in response to Vitamin A and Vitamin D. We have considered the positive effects these three vitamins have on bone development, teeth and the immune system. Vitamin A works with Vitamin D to promote healthy gene function and limit prostate cancer. Vitamin D and Vitamin K both contribute to good mental health, sound cognition, and healthy nerves. Vitamin A and Vitamin K contribute to healthy and younger looking skin while protecting from skin cancer and keeping wrinkles at bay.
One can expect noticeable holistic health improvements in the short-run as well as considerable benefits in the long-run. This trio makes for an effective combination and should be a core component of any supplement strategy. Here are the areas where these vitamins work together.
 We considered how these vitamins create demand for each other. Taking Vitamin D alone can cause a deficiency in Vitamin K2 because more Vitamin K2 is needed for bone forming activities triggered by Vitamin D. Moderate amounts of Vitamin D increase the body’s need for Vitamin A. Both Vitamin A and Vitamin K help protect against the negative effects of rare Vitamin D toxicity. Not only do these ADK vitamins work well together to maintain good health, they also protect you from toxicity and negative side effects.
We considered how these vitamins create demand for each other. Taking Vitamin D alone can cause a deficiency in Vitamin K2 because more Vitamin K2 is needed for bone forming activities triggered by Vitamin D. Moderate amounts of Vitamin D increase the body’s need for Vitamin A. Both Vitamin A and Vitamin K help protect against the negative effects of rare Vitamin D toxicity. Not only do these ADK vitamins work well together to maintain good health, they also protect you from toxicity and negative side effects.
.
.


