Radiation Health Risks
Part III – Mitigating the Risk
Life with Geiger counters will become much more common
in our futures as well as nuclear weather reports.
-Dr. Mark Sircus
In Part I we discussed ionizing radiation and how it poses health risks to humans. In Part II we looked at contributing factors of radiation dosage and the sources of ionizing radiation. In this section we discuss the importance of iodine supplementation and how to protect against the harmful radiation under normal circumstances.
Importance of Iodine Supplementation
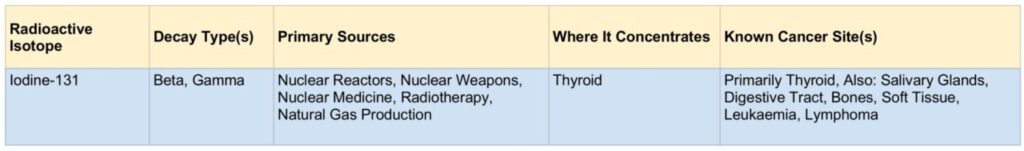
Iodine can significantly reduce the radiation health risks associated with Iodine-131. Iodine-131 produces beta-particles and gamma-rays. It decays quickly, is highly radioactive and emits a high amount of energy. Iodine-131 has a relatively short physical half-life of 8 days when compared to other radionuclides. This does not necessarily make it less dangerous. If you are far away from the original source it is less of an issue because by the time it reaches you the radioactive components will have been greatly reduced. However, if you are close to the original source it will be very destructive to tissues as Iodine-131 releases a great deal of energy in a short time span.
Iodine-131 is used in medical diagnostic and treatment procedures, nuclear energy, nuclear weapons, and industries such as natural gas production.
Medicine
Iodine-131 is often used in high doses for therapy to kill cells, especially thyroid cells. Patients should be careful with low doses, for example with Iodine-131 thyroid tracers, because it presents a higher risk of cell mutation.
Nuclear Reactors
Iodine-131 was a significant contributor to the health hazards from the Chernobyl disaster and other disasters. Much of the contamination hazard in the first weeks in the Fukushima nuclear crisis was from Iodine-131. The same is to be expected from any such incidents in the future.
Nuclear Weapons
Iodine-131 is common in the fallout from nuclear weapons. High levels of Iodine-131 in the environment from radioactive fallout can be absorbed through contaminated food, and will also accumulate in the thyroid.
Industrial Applications
Iodine-131 became one of the most commonly used gamma-emitting industrial radioactive tracers. It has applications in estimating the age, origins and movement of water, as well as detecting leaks.
Beta-particles and gamma-rays from Iodine-131 are effective in both killing cells and causing mutations. These risks are mitigated by taking iodine supplements. By raising the total amount of iodine in the body you will reduce the body’s uptake of Iodine-131. Preventing uptake by saturating the body and thyroid with non-radioactive iodine is called iodine blocking or thyroid blocking. Excess iodine, including unabsorbed Iodine-131, will be excreted in the urine. The form of iodine commonly used for thyroid blocking is Potassium Iodide (KI).
Dr. David Brownstein has said 13 mg of iodine per day prevents approximately 96 percent of radioactive iodine from binding to the thyroid gland. According to governmental planners, iodine supplementation with potassium iodide works best only two hours before or up to four hours after exposure to radioactive iodine. Your best bet is to stay ahead of things by supplementing with iodine daily while getting all of the health benefits of doing so. In the event of certain radiation exposure or radiation emergency one should seek out medical assistance immediately by contacting your doctor or emergency services. Iodine supplementation is not a substitute for using FDA-approved iodide tablets in the event of radiation exposure or emergency.
Regular iodine supplementationwill help keep higher levels of iodine in the body. It is also very easy to do and promotes good health.
Other Ways to Reduce Radiation Health Risks
Mitigating radiation risks should be consistent and ongoing. Regular iodine supplementation will help keep body iodine levels high. Here are some measures that may reduce the risk of radiation sickness in the short- and long-run.
Understand the Risks Associated with Medical Procedures
Take the time to clearly understand the risks of medical procedures involving radiation. Determine if it is a low or high dose treatment. Inquire about fractional dosing and the trade-offs for it compared to higher doses as it applies to your situation. Learn about the radioisotopes being used. Gauge the likelihood of positive outcomes as well as the probability of unintended negative outcomes. What other sources of radiation have you been exposed to? Mammograms, X-rays, working around radioactive material etc.. Radiation accumulates in the body so all sources should be considered when assessing the risks. Make your doctor explain everything, weigh the risks and benefits for yourself and then consider their recommendation. If it leads to more questions then ask. Your health is valuable so it is worth your time to investigate. These procedures are often very profitable so it is worth the doctors and technicians time to explain the details. There is no reason to not have a thorough discussion and understanding of any radiotherapy and/or nuclear medicine procedures being considered.
Stop Smoking and Avoid Secondhand Smoke
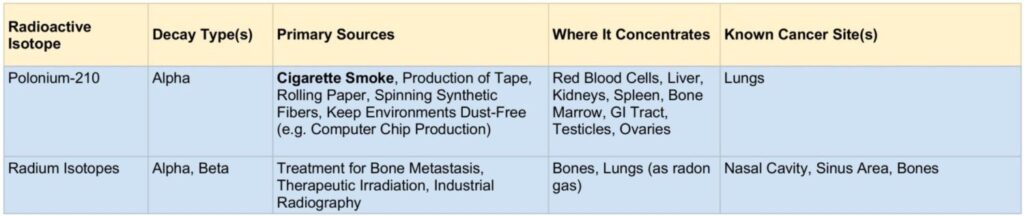
This may seem like an obvious good-life-decision but let’s look at why it is important with respect to radiation. Smoking exposes you to radiation directly. Note, in the table of radioisotopes shown in Part II, smoking is listed as a source of the radioisotope Polonium-210. Moreover, smoking greatly increases your susceptibility to the radiation risks of radon gas. Smokers and those regularly exposed to secondhand smoke have 6-7x higher risk of lung cancer from radon gas.
Advocate Political Views With The Aim of Reducing Potential for Nuclear War
Since discovering radiation we have been on a steady path to more sources and higher levels of nuclear threats. Nuclear bomb detonations and its fallout contaminate much our biosphere. Ocean currents, jet streams as well as the movement of people and agricultural goods means exposure from nuclear weapons and military strikes is never isolated to a single region or continent.
You can also join the Anti-Nuclear Social Movement. This includes many organizations around the world and across the US. All are opposed to nuclear weapons and some are also opposed nuclear energy.
Here are some examples of international organizations engaged in this work.
International Campaign to Abolish Nuclear Weapons
International Physicians for the Prevention of Nuclear War
Union of Concerned Scientists
Friends of the Earth International
There are many similar organizations in the US. This group includes:
Physicians For Social Responsibility
Economists for Peace and Security
Council For A Livable World
Mothers For Peace
Musicians United For Safe Energy
The nuclear responsibility movement is very accessible. There is something for everyone.
Own A Geiger Counter
 This is a great preventative measure since we cannot detect ionizing radiation with our senses. It is especially helpful if you or someone you know works around radioactive materials, such as in hospitals or nuclear power facilities. Though it is unlikely that your home and surrounding areas have dangerous levels of radiation, early detection could save you and your community a great deal of hardship. Plus, having peace of mind goes a long way. In the event of a nuclear emergency, you will have a useful tool for detection at your disposal and hopefully you will already be on iodine supplementation,
This is a great preventative measure since we cannot detect ionizing radiation with our senses. It is especially helpful if you or someone you know works around radioactive materials, such as in hospitals or nuclear power facilities. Though it is unlikely that your home and surrounding areas have dangerous levels of radiation, early detection could save you and your community a great deal of hardship. Plus, having peace of mind goes a long way. In the event of a nuclear emergency, you will have a useful tool for detection at your disposal and hopefully you will already be on iodine supplementation,
These measures are for normal circumstances. In the event of a nuclear emergency much more needs to be considered. You may want to have an understanding of subjects like radiation shielding, survival essentials, and adequate food storage.
.
Summary
Ionizing radiation has enough energy to alter the structure of atoms and molecules. These changes can kill healthy cells and corrupt DNA leading to genetic mutations and cancer. The tissues most sensitive to radiation are those with rapidly-dividing cells. High doses of radiation are more effective at killing cells. Low doses of radiation pose a greater long-term risk of unwanted mutations and related genetic diseases like cancer. Radioisotopes concentrate in areas of the body that normally absorb materials of a similar chemical structure. Ionizing radiation is often used in medicine for diagnosis and treatments, industry, agriculture, and nuclear power facilities. It also is central to the function of nuclear weapons and remains present in the aftermath. Supplementing with iodine regularly helps the body maintain a higher level of iodine and may help block the absorption of unwanted forms of iodine. Other ways to reduce radiation health risks include avoiding cigarette smoke, being selective for medical treatments involving radionuclides, advocating against nuclear war, and owning a Geiger counter to detect high-levels of radiation.
It is our hope that as nuclear technology improves, the benefits will far outweigh the risks. We stumbled upon an abundant source of energy, however with its great destructive capacity, we must grow into the role of being the custodians of the planet. Maybe this mushroom cloud of a situation has a silver-lining. Since it is hazardous to all humans, and is a more immediate threat than climate change, it may nudge us towards increased global citizenship, re-thinking our values and identifying more with all of humanity. Though there is still room for optimism, the near-term risks are significant and there are many reasons to be cautious. Taking precautions will not only reduce the health risks, but also ease the mind and limit any psychological damage that too much worrying can cause.
.
.


